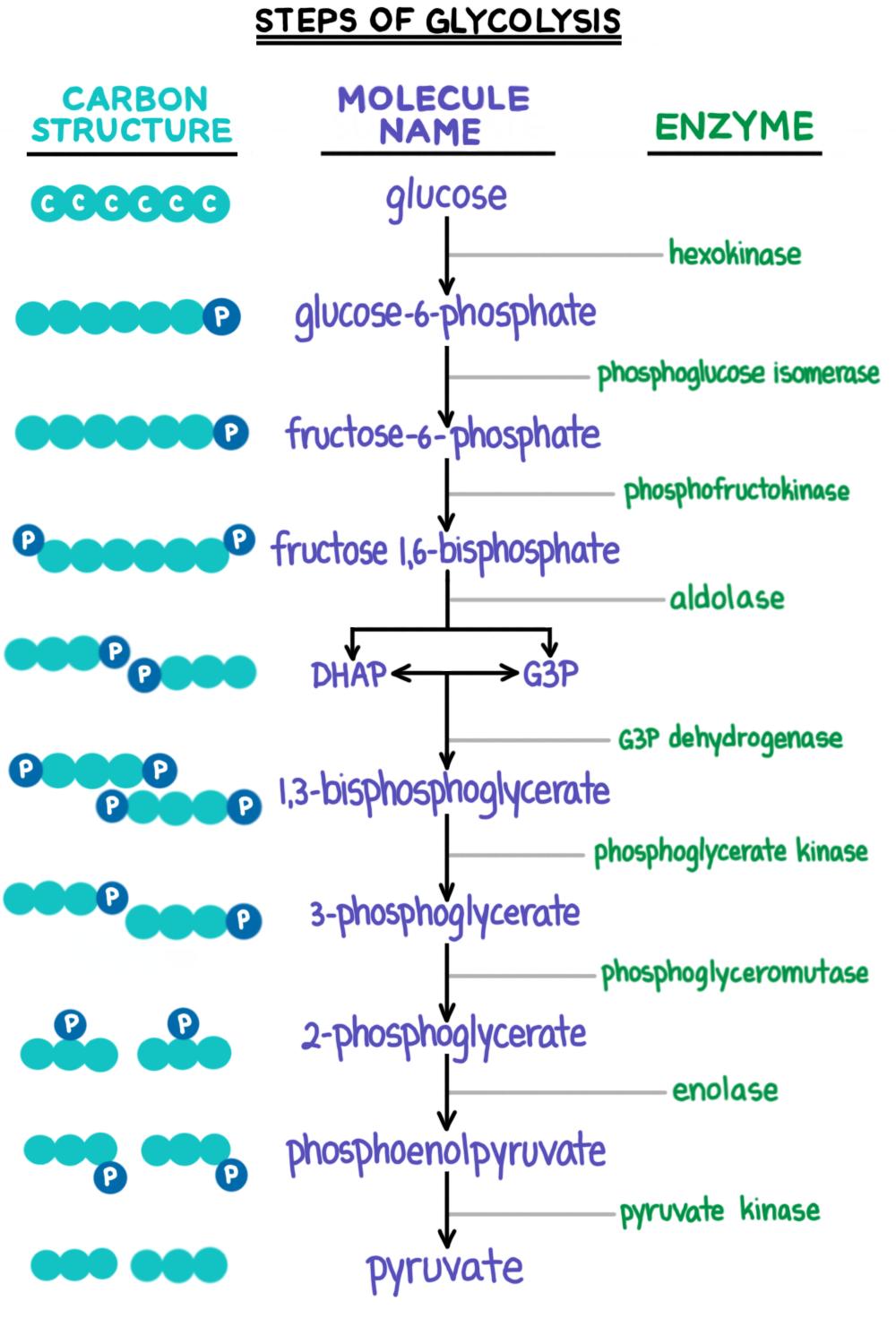
The Reduced Form Of The Electron Acceptor In Glycolysis Is - This allows glycolysis, which requires the oxidized electron acceptor nad+, to continue. If a is molecular oxygen, water (ah) will be produced. Web in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic glycolysis) nadh generated by glycolysis is reoxidized to nad + by donation of its electrons to reduce pyruvate to lactate, which enters the blood. In this case, complex ii can also translocate a proton during the process. Web so, if a h atom and its electron join a molecule, odds are that whatever's bonded to the new h is going to hog the electron and become reduced. Web the reduced form of the electron acceptor in glycolysis is [nadh] energy from glycolysis among the products of glycolysis, which compounds contain energy that can be used by other biological reactions? Web complex ii red reduces a, the terminal electron acceptor to regenerate complex ii ox and create the reduced form of the terminal electron acceptor. Web the second part of glycolysis extracts energy from the molecules and stores it in the form of atp and nadh, the reduced form of nad. O is more electronegative than any of the other major atoms found commonly in biological molecules.
O is more electronegative than any of the other major atoms found commonly in biological molecules. This allows glycolysis, which requires the oxidized electron acceptor nad+, to continue. In this case, complex ii can also translocate a proton during the process. Web in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic glycolysis) nadh generated by glycolysis is reoxidized to nad + by donation of its electrons to reduce pyruvate to lactate, which enters the blood. If a is molecular oxygen, water (ah) will be produced. Web so, if a h atom and its electron join a molecule, odds are that whatever's bonded to the new h is going to hog the electron and become reduced. Web complex ii red reduces a, the terminal electron acceptor to regenerate complex ii ox and create the reduced form of the terminal electron acceptor. Web the second part of glycolysis extracts energy from the molecules and stores it in the form of atp and nadh, the reduced form of nad. Web the reduced form of the electron acceptor in glycolysis is [nadh] energy from glycolysis among the products of glycolysis, which compounds contain energy that can be used by other biological reactions?