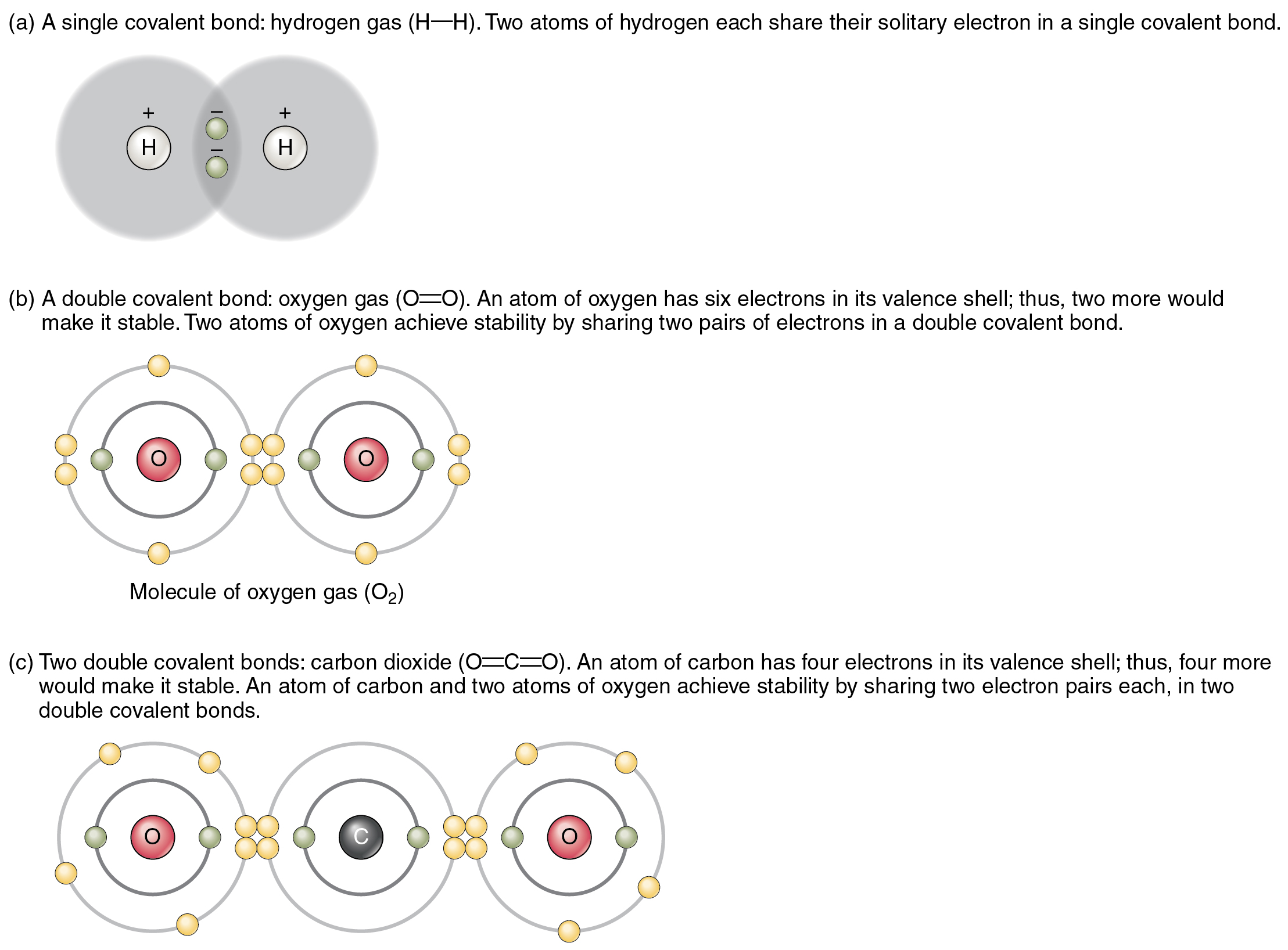
Two Hydrogen Atoms Form A Hydrogen Molecule When - Each hydrogen atom in the h 2 molecule has. Covalent and ionic bonds are intramolecular forces. Web two hydrogen atoms can combine by donating each of their electrons into a single covalent bond, depicted on the right as the. Hydrogen bonds are intermolecular forces; Web for example, two hydrogen atoms bond covalently to form an h 2 molecule; Web for example, two hydrogen atoms bond covalently to form an h 2 molecule; Each hydrogen atom in the h 2 molecule has. Web the hydrogen atoms are bound to the highly electronegative oxygen atom (which also possesses two lone pair sets.
Web two hydrogen atoms can combine by donating each of their electrons into a single covalent bond, depicted on the right as the. Web for example, two hydrogen atoms bond covalently to form an h 2 molecule; Web the hydrogen atoms are bound to the highly electronegative oxygen atom (which also possesses two lone pair sets. Web for example, two hydrogen atoms bond covalently to form an h 2 molecule; Each hydrogen atom in the h 2 molecule has. Hydrogen bonds are intermolecular forces; Covalent and ionic bonds are intramolecular forces. Each hydrogen atom in the h 2 molecule has.